Description
Urine tests can provide diagnostic information about a number of diseases such as kidney disease or infections, diabetes, and liver disease. The urinalysis consists of 3 parts: measuring the urine concentration using a refractometer, using a test strip to quantify protein, blood, glucose, etc., and a microscopic examination to detect cells and crystals.
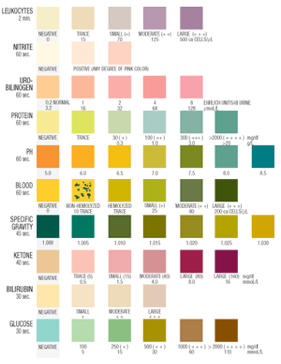
Urine test strip
- Blood can be identified on the strip in hemolyzed form, which is not seen under a microscope.
- Glucose in the urine can indicate diabetes.
- Ketones can indicate ketoacidosis, which is a serious problem.
Microscopic examination
The numbers and types of cells and/or material such as casts can yield a great detail of information.
- Red blood cells are associated with kidney infections, bladder infections, bladder stones, interstitial cystitis, and renal infarcts.
- White blood cells are associated with bladder and kidney infections.
- Casts can be associated with various illnesses, depending on the type.
- Crystals can be associated with bladder irritation.
- Bacteria can be associated with an infection of the bladder or kidneys.
Refractometer
The refractometer detects urine concentration. Dilute urine can be see with kidney disease and other illnesses.